
Low download speed can be a real bummer in a digital world, especially if you’ve paid for high-speed internet and can’t figure out what’s triggering the situation.
When your download speed is too low, there could be multiple culprits, from router settings to ISP shortcomings and physical damage to your wires and devices.
Read on to diagnose and eliminate what’s slowing yours down.
Download Speed Suddenly Slow (Causes, Fixes)
1. Overheat Or Overrun Device
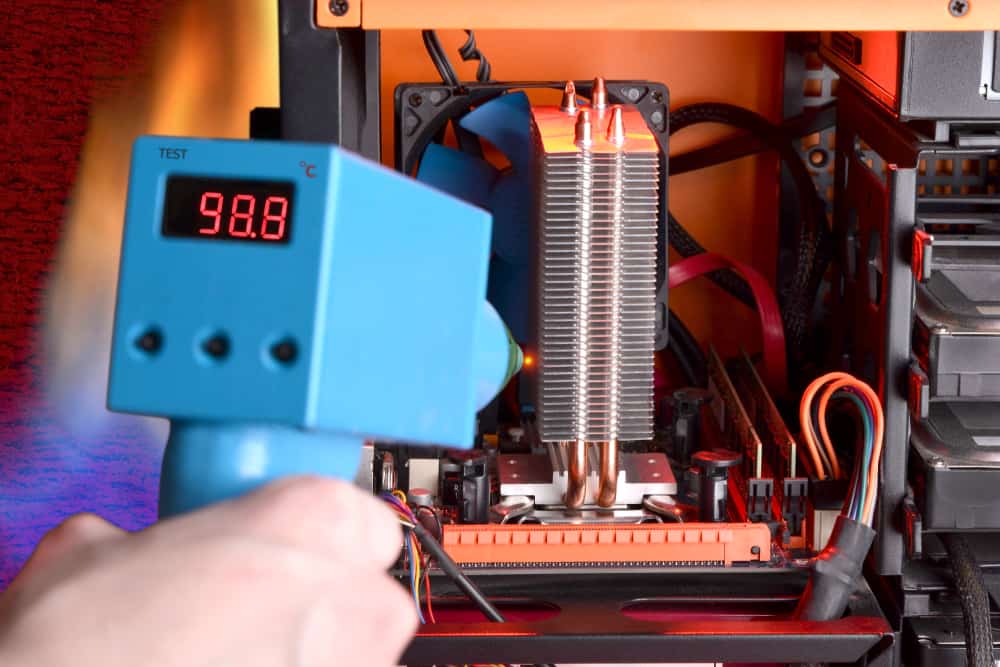
Sometimes, your electronic devices start behaving strangely, thus halting or decelerating some functions.
In these cases, you have to give them a kick-start by rebooting the system.
A restart flushes the RAM, reduces CPU usage, and fixes minor low-level glitches.
You should restart any device that’s part of your connection, including your router, computer, mobile phone, etc.
If using the “reboot” key doesn’t work, manually turn off the device, detach it from the outlet, and wait a few minutes before you reconnect it.
2. Wrong Placement Of Router

Although often neglected, the distance between your router and your device has an essential role in your internet performance.
The closer you get to the router, the stronger the signals, and therefore, the higher your internet speed.
Position your router somewhere at the center of the house or where you usually sit and tackle your internet-hungry tasks.
If moving your router isn’t an option, try extending the antenna in another direction or adding a WiFi extender.
This will reinforce your WiFi signal, push it further, and distribute it at different angles.
However, positioning your router isn’t only about distance.
You also have to eliminate physical obstacles between you and the router since the WiFi signals cannot pass through hard objects such as metal furniture, cement, or concrete walls.
Not only that, radiation-emitting gadgets such as TVs, microwaves, Bluetooth, and wireless devices can interfere with your Wi-Fi signals, slowing down your speeds.
Do your best to keep them at bay.
3. Low Connection Speed

The speed your ISP claims to offer is only applicable in ideal situations where there are no crowded websites, rush hours, or logical and physical defects with your devices.
In reality, your speed may be far less than the stated megabits.
Run a speed test before anything to see if you can pinpoint the source of your problem early on.
Speed.net is a free tool that lets you evaluate your download/upload speed in real time.
After getting the results, continue as follows:
Redo the test while connected via an Ethernet cable
You need to test your internet speed twice: Once when you’re directly connected to the modem via cable, and once when you’re using WiFi.
Then, analyze the differences.
If you see a considerable gap, chances are your router is faulty.
Skip the next steps and head forward to the “Router Breakdowns” section.
Compare the reported speed with what you actually need
Broadbandnow is a tool that calculates your required internet speed.
Just open the website and insert the number of internet users and devices you have in your household.
Then, report the type and frequency of your activities.
It’ll advise you about the best speed you can get to fulfill your demands.
If the recommended amount is considerably higher than what you’re getting, contact your ISP to upgrade your internet plan.
Compare the numbers with those provided by your ISP
If you see a significant contrast between the results and what your ISP has promised—for example, your package is 30 Mbps, but the speed test shows something around 5 Mbps—perform a website check.
It shows you whether the issue is with a specific server or it’s just your service provider.
Then, let your ISP know about the mismatch.
They’ll check if the trouble lies within your home, your location, or their company’s back end.
4. Running Out Of Data

Some ISPs, including satellite internet providers, have an upper limit for their plans.
That means, if you use more than a certain limit, they reduce your internet speed to near zero until you buy more data.
Ensure you haven’t surpassed the data cap, and then continue with the next workarounds.
5. Multiple Connected Devices

Look over the time your internet gets suddenly slow: Does it coincide with when everyone in the household arrives home?
Is it happening mostly at night when everyone returns from work and starts surfing the net, checking their social media, and streaming videos?
If so, then your bandwidth is to blame for your low-speed problems.
To help you understand the problem, let’s give you an example.
Imagine the road that leads people, vehicles, and goods to your house.
Just like any other route, it has a certain capacity and may get blocked if too many people try to move along it.
Ten cars can never reach your house as easily as a single one does.
If you want to prevent or mitigate the traffic, you have no other choice but to decrease the number of vehicles or find a way to widen the road.
Bandwidth is exactly the same as this road.
If it’s too low, it can’t handle the data traffic your housemates are creating.
The first way to overcome this situation is to buy an internet package with higher bandwidth, ideally 5 GHz.
If you don’t want to make a large investment, you can also try the following tricks to increase your bandwidth:
- Disconnect not-in-use devices: These include your kitchen appliances, speakers, consoles, etc., as well as laptops, tablets, and smartphones that are not currently in use.
- Restrict the bandwidth for some users: Setting guest networks for kids and non-family members prevents them from eating up your bandwidth.
- Take turns: Assign a specific download time for every member so that everyone gets a chance to use the bandwidth exclusively.
- Download at a later time: While you cannot delay some routine online tasks, downloads can wait a few hours.
Set your device to automatically download files after midnight when everyone else is asleep.
Alternatively, postpone your downloads to a time when everyone is out.
6. Network Congestion

Network congestion is the same as device overcrowding but on a larger scale.
It happens when multiple nearby households use the same network (ISP), and as a result, the provider can’t handle the data flow to and from that area.
This situation gets worse during peak or rush hours—early evening to a while after midnight—and leads you to more bandwidth competition.
Unlike household congestion, you can’t set limits on when and how others use the network in this case.
You have no option but to give up on your current ISP.
Ideally, you can change your internet type since cable internet suffers from such issues more often.
For example, with fiber internet, you don’t have to share bandwidth with others near you.
However, note that satellite and DSL networks have their own problems, including latency.
Do your homework before signing up with a service provider.
7. Active Background Applications

Bandwidth consumption isn’t limited to home devices and the number of users in your area because too many applications on a single device can also take up all your bandwidth.
Utilities such as Windows Update and Google Play Store that automatically download several files are great examples.
Gaming and video streaming apps also consume a lot of data and take their toll on your download speed.
Other than devouring your bandwidth, active applications can hog your PC’s processing memory, which is responsible for your downloading capacity.
If you disable these idle apps, you’ll free up both memory and bandwidth, boosting your download speed:
- Use your Windows search tool to get to the Task Manager.
- Select the “Processes” tab to see a list of your active apps.
- Close any idle app that comes to your notice by hitting “End Process.”
- Be careful not to terminate critical System, Windows, and Microsoft processes like explorer.exe.
8. Poorly Protected Network

There’s always the chance that someone may be secretly using your connection, especially if you experience speed lags many times a day and at different hours.
This is more likely if you’re using the router’s default password, but even if you have a different password, anyone with little programming experience can hack it.
The first step to rule out such threats is to change your router’s administrative credentials.
Then, switch to a stronger type of encryption.
WPA2-AES encryption is more reliable and offers you more resistance to unauthorized access.
Watch this video to learn more about WiFi password types.
Video:
If these tips resolve your internet slowdown, tweak more WiFi settings to guarantee your future safety and keep the intruders at bay.
Also, always try to set a more hard-to-guess password for your router.
9. Virus And Badware Infection

Broadband hijacking can also happen as a result of malware infection.
It’s a good idea to have a trusted antivirus on your system and actively scan potential threats.
Make sure it has spyware detection capabilities and keep it up-to-the-minute.
Here are a few suggestions:
10. Wrong WiFi Band

Even if you pay for high bandwidth, it won’t work unless your devices can support the range.
By devices, I mean both the router and your connected systems.
First off, make sure you have a Dual Band Router or one that’s designed to work with a 5 GHz frequency.
Then, ensure your laptop, smartphone, etc., have the ability to cover the 5 GHz band.
Notice that even if they do support the 5 GHz frequency, they may decide not to connect to it due to specific reasons (such as your location, frequency strength, congestion, etc.).
You will have to open network settings on that device and manually pick the band you want:
Jump to your router administration page and visit its Settings or Setup section.
Navigate to the Bandwidth Allocation field and find a way to mark the 5 GHz somewhere in the configurations. (You may find it in a different section depending on your ISP.)
How To Access Your Router’s Admin Panel
- Open a browser of your choice, type your router’s IP in the address bar, and press Enter.
Note: You can usually find your IP address and other login credentials at the bottom of your router, but if you’ve changed it, or the descriptive sticker has peeled off, you can find it via these methods.
- Input your username and password in the empty fields.
Note: both username and password are “admin” in most cases, but try some alternative ways to find it if that doesn’t work.
Video:
11. Overlapping WiFi Channel

A WiFi channel is like an avenue through which a router transmits data.
You can find several channels in each frequency range: Eleven channels in the 2.4 GHz band and as much as 45 in the 5 GHz spectrum.
However, since most routers automatically connect to a random channel at their initial setup, one or more channels may get more crowded than others.
When this happens, wireless networks start impeding or conflicting with each other, minimizing their speed.
You have to ensure you’re not on this overflowing channel.
WifiInfoView (for Windows), Wireless Diagnostics (for Mac), Wifi Analyzer (for Android), and Network Analyzer Lite (for iOS) are pretty helpful with this issue.
They help you check if your existing channel is overloaded and list other available channels so you can pick the one with the least traffic.
Note: Once you choose the best channel, you have to visit your router’s administration page to change it:
12. Using VPN

Many users rely on VPNs to enhance their security, privacy, and accessibility.
Although beneficial, these tools can wreak havoc on your speed because they establish a second tunnel for your data to pass over the internet.
This way, your network has to handle more information, and your plan may fail to compensate for the additional processing.
Turn off your VPN to see if the issue disappears.
If VPN is necessary for your downloads, switch to better software because not all VPNs provide the same speeds.
Plus, premium versions are usually more efficient than free ones.
You can also adjust your VPN to another region if it helps.
13. Wires And Connections

Computer networking involves so many wires, phone jacks, pins, and connectors, and if any of them get faulty, your connection becomes unstable.
Check all the connections from top to bottom and, if needed, replace your ports, outlets, Ethernet, and coaxial cables.
If the issue persists, ask your cable provider to probe your cable box, splitter, and the lines going from the street to your place.
Sometimes, an internet lag occurs due to a power outage or a cable defect in your neighborhood.
Other times, it comes from your own electrical wiring.
In both cases, a technician can help.
14. Router Breakdowns

As your connection’s main mechanism, the router can be a culprit for your internet dropouts.
Whether it’s old, cheap, defective, or just improperly configured, you can optimize this instrument using the following hacks:
A. Update The Firmware
Like other hardware, your router might not work optimally if you don’t update it.
Plus, updating your router’s firmware can fix the unknown bugs and enhance its speed, performance, and security:
- Use a browser and input your login details to open the router’s admin page.
- Look for a section labeled as “Management,” “Advanced,” “Administration,” or something along the lines.
- Then, navigate to the “Firmware” or “Update” settings.
- Check if the interface provides an automatic search tool for the latest firmware.
- If so, use it to find and install the newest firmware.
- If not, visit the manufacturer’s support site, and insert your router’s model to get the related files manually.
- Now, find a way to upload the files in the Administration “Update” section.
Note: You may have to unzip the file before uploading it through the “Browse” button.
B. Tweak More Configurations
If updating firmware doesn’t help, ensure your other router’s configs correspond with what is suggested by the manufacturer.
If you don’t access your manufacturer guidelines, click here and assign everything accordingly.
You can also give these methods a shot:
- Enable WMM Settings.
- Adjust your RTS threshold to a lower value if you live in a crowded house.
- Decrease the numbers for your fragmentation threshold.
- Disable “Optimize AMPDU Aggregation.”
- Increase your MTU parameter.
- Heighten your TCP packet size, but don’t let it exceed the MTU.
C. Factory-Reset Your Router
Reverting your router to default settings can be your last effort before you consider replacing it.
Use a sharp-end object such as a pin to press the itty-bitty button at the back of the machine, holding it for about ten seconds.
Wait for the blinking lights or any other signs that verify your router has been successfully reset.
Continue to your network admin panel to reassign your Wi-Fi name, password, etc.
D. Buy New Equipment
Just like any type of electronic equipment, routers wear thin after a while, and this process occurs sooner if you own a cheap one.
If your internet is slow, try buying a router with top-notch quality.
NEXT: Mouse Randomly Clicks (Causes, Fixes)


























chujowe nie pomogło
dyduch co ty pierdolisz