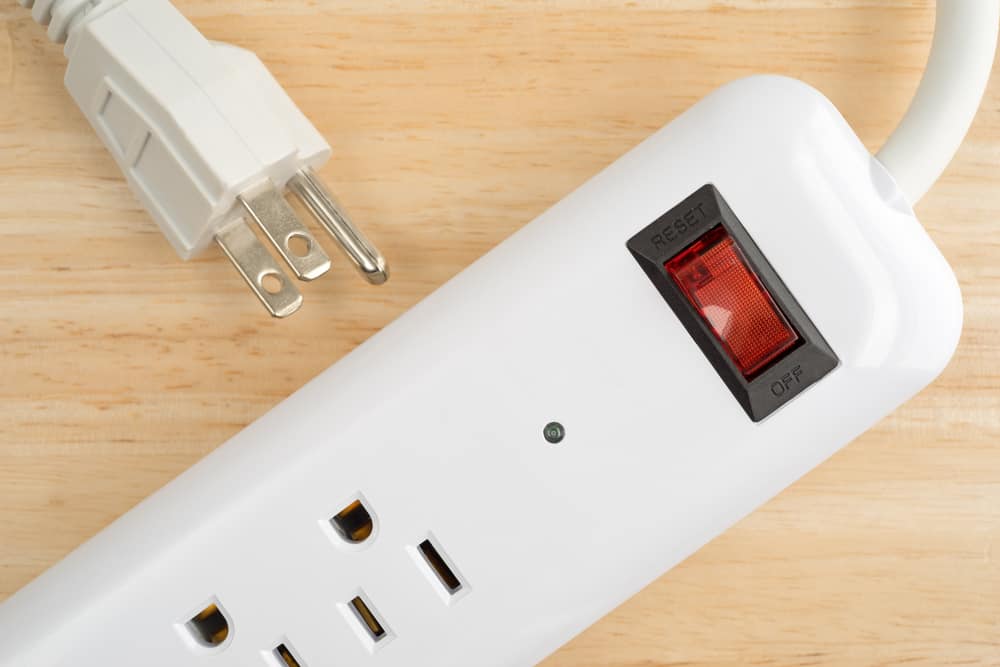
Protecting your expensive electronics is a must, especially if you live in a region with an unreliable power grid or constant outages due to weather conditions.
A good old surge protector may do the trick to ensure your devices remain safe during these emergencies.
An Uninterruptible Power Supply (UPS) is a more reliable failsafe to make sure your critical devices continue working properly.
Can you combine these two methods to double the safety measures?
This article will talk about whether it’s possible to plug a surge protector into a UPS.
We’ll also talk about their differences and when to use which one.
Can You Plug A Surge Protector Into A UPS?

You may decide to plug a surge protector into your UPS to get more outlets to plug in more devices or have extra protection.
Some technicians believe that you can safely plug the surge protector into a UPS.
They think by plugging the surge protector into the UPS, you’ll simply add a breaker to the circuit before the current reaches the UPS.
It doesn’t damage your system, and you shouldn’t be afraid of it.
However, it’s not necessary because the UPS will do the surge protection natively.
However, in the interest of safety, it’s always recommended to plug your UPS directly into a wall outlet.
Here’s why.
Surge protectors have a noise filtration circuit that can cover some of the UPS load.
As a result, the UPS won’t show the true attached load, reporting a lower percentage.
It may trick you into using more devices, overloading the UPS.
That’s particularly troublesome when the UPS runs on battery.
It can’t support the devices attached to it and will cause a load drop.
Plus, UPS can handle a limited number of devices.
When you plug a surge protector into it, you increase the number of receptacles and the devices plugged into it.
This way, you may cause an overload.
Each UPS has a specific load limit that you can find in its user manual.
Check the wattage consumption of your devices and make sure you’re not overloading the UPS.
Another reason is that this is like daisy-chaining devices, in which you connect one surge protector into another.
This will draw too much current, resulting in more heat and probably fire and damaged equipment.
When you plug different surge protectors into each other, the electrical current that runs through them exceeds the allowed and safe amount, causing the circuit breaker to trip or start a fire.
Depending on the jurisdiction, some fire codes consider it a violation because they consider it a daisy chain.
A UPS is technically regarded as a surge protector, s
o you should treat it like one in this matter.
In addition, some UPS brands clearly state that if you use a surge protector with the UPS, you’ll violate the safety instructions, and your warranty will be void.
Can I Plug A UPS Into A Surge Protector?

You may decide to protect your UPS from power surges by plugging it into a surge protector because it never hurts to be super cautious.
The thing is, you don’t need to do that, and you shouldn’t.
Unless you plug the UPS directly into a wall outlet, it won’t get the best power supply possible.
The main reason is that you may plug more devices into the surge protector.
In this case, some of the more powerful ones draw away some voltage necessary for the UPS to remain online.
Therefore, it will go to the battery while it should remain online, reducing its battery runtime.
Plus, ground protection is vital for the UPS to provide enough surge protection.
Plugging it into a surge protector may tamper with it, reducing the efficiency of the UPS.
Can I Plug A UPS Into A Power Strip?

You shouldn’t plug your UPS into a power strip to increase the number of receptacles.
The main reason is the overload problem due to the increased number of devices.
Sometimes you have physical limitations, such as a distance from a wall outlet and the device plugged into the UPS, s
o you might want to use a power strip to provide better access.
Using a power strip is less risky than a surge protector because it doesn’t have any protection capacity.
If you use a power strip, don’t fill it to the full capacity with other devices.
Ensure you only plug the UPS into it to prevent other devices, especially the more powerful ones, from drawing more power.
Alternatively, you may decide to plug the UPS into the wall outlet and plug the power strip into the UPS.
This way, you’ll have more freedom in terms of the distance from the wall.
This method isn’t recommended because it may reduce efficiency.
It’s always better to connect your equipment directly to the UPS and not to a power strip.
If you choose to do so, make sure to stay within the capacity of your UPS to avoid overloads.
What Should Be Used Instead?

If you have to add to the number of receptacles, use a power distribution unit instead of a UPS.
Surge protectors look for power surges and filter them out, but they don’t distribute the amperage efficiently.
That will cause some of your devices to shut down or reboot because they don’t get enough power.
On the other hand, power distribution units distribute the power evenly among all devices.
They don’t filter power surges, and they don’t need to because it’s the UPS’s job to provide power protection.
This way, you’ll protect your devices from power surges and distribute the power efficiently across all of them.
Alternatively, you can use a surge protector and a UPS independently for different devices.
For example, use a UPS for more critical, sensitive equipment such as your PC or other devices for which you will lose your work and other important data in the event of a power outage.
Plug other devices such as printers or copiers into a surge protector to have peace of mind in case of power surges.
What’s The Difference Between A Surge Protector And A UPS?

Power interruptions are responsible for considerable damages to electronic devices, especially computers.
The problems caused by power interruptions aren’t limited to physical damages, though.
In the case of computers, it can lead to permanent data losses, which, in turn, could lead to economic losses.
Lightning, problems in the grid system, and even human errors can lead to these power interruptions.
For example, you may accidentally plug out a major device, only to find out you’ve lost critical data.
The good news is that such problems have simple solutions.
Surge protectors and UPS units are here to protect our devices from these problems.
A surge protector guards your devices against power drops due to voltage spikes.
When a voltage spike occurs, the surge protector will send back the extra current into the grounding wire running through the outlet.
In addition to voltage spikes, a surge protector can protect your devices against other issues such as blackouts, noise, and burnouts.
Blackouts refer to complete crashes of the electric grid resulting from overconsumption or natural disasters such as floods.
Brownouts refer to drops in voltage, leading to less power.
While blackouts and brownouts are equally destructive, they’re different conditions.
Noise refers to the voltage spike caused by instances such as lighting.
Although it may seem minor, it can damage the sensitive circuits in our electronics.
The surge protector can protect your devices from these power-related problems by breaking the current and not allowing it to enter your devices.
What about other problems such as lost data?
Once your computer turns off, you’ll miss any unsaved data.
Suppose you’re working on your laptop, and there’s a sudden power outage.
You can’t be bothered because your laptop works on a battery, and you won’t lose any data.
What about a desktop computer that doesn’t work on batteries?
Here’s where a UPS comes to help.
Also known as a battery backup, an Uninterruptible Power Supply (UPS) doesn’t allow your devices to shut down suddenly in case of power failure.
When a power outage occurs, the UPS ensures your connected devices don’t experience any interruptions by working off the battery.
You may not be able to use it for a long time since the battery will eventually die, but it gives you some time to switch to another power source or save your data and shut down your devices normally.
You should know that a UPS can’t be a sole source of power for a long time, such as during an extended blackout or a natural disaster.
How Do You Choose A Suitable UPS?
There are different kinds of technology used in UPS devices.
Standby constantly monitors the current to find inconsistencies in the most basic way.
It switches to battery when it detects a power surge or outage.
This way, your devices will continue operating on battery without any interruption in power.
This type of UPS is suitable for basic computers, security systems, consumer electronics, and POS systems.
Line-interactive corrects minor electricity fluctuations such as surges or drops but doesn’t switch to battery.
It uses an autotransformer to regulate such fluctuations.
It’s a solution to long-term electrical problems by stabilizing the current and provides power during blackouts and brownouts.
Consumer electronics, home theater devices, gaming systems, and PCs can use this model of UPS.
A double-conversion UPS ensures your devices have access to consistent power whether there are fluctuations or not.
Operating on isolated DC power, it converts AC power to DC and changes it back to AC.
When you plug a device into an online UPS, it isolates the device from the wall power by constantly filtering the power through its battery system.
This way, you can make sure the device never gets an interruption, even for a millisecond.
Since it doesn’t need to switch to battery and DC power, it has no transfer time, leading to high efficiency.
Also referred to as online TPS, this type of UPS is perfect for mission-critical IT devices, high-end servers, advanced network installations, and data center equipment.
It’s the most expensive type of USP because it needs more complicated circuits.
In addition to the type of technology suitable for different devices, UPS manufacturers clearly state that users shouldn’t connect their devices to certain equipment.
For example, CyberPower says that using their products with high-drain devices and medical and aquatic equipment will void the warranty.
Plus, laser printers, paper shredders, copiers, vacuums, and curling irons also void the warranty.
Other essential considerations in picking the right UPS are the number of outlets, displays, and fans.
For example, the number of outlets depends on the number of devices you need to connect to the UPS.
UPS units feature both on-battery and off-battery outlets.
Some UPS units are specific to modems and routers because these devices need ports for coax and ethernet cables.
Some of the higher-end UPS units come with replacement batteries to use when the battery fails.
When you want to choose a UPS, you should consider all these factors.
Power Strips Versus Surge Protectors
A surge protector and power strip may look exactly like each other.
Both provide more outlet options to plug different devices into them.
However, unlike a surge protector, a power strip doesn’t protect against power surges.
If you don’t use a UPS to protect your devices, the choice between a power strip and a surge protector leans towards the latter.
You don’t want to damage your devices due to power fluctuations because you can’t predict when they happen.
A power strip is just like a wall outlet, only looking different.
NEXT: Why Is My Firestick So Slow? (Reasons, Fixes)